Fulfilment costs encompass various elements such as storage, shipping, and handling fees. By optimising these expenses, businesses can improve their profit margins, offer competitive pricing, and deliver a better customer experience. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers play a significant role in this, with their various fees and shipping strategies.
This guide explores the different factors that influence 3PL costs, including storage and fulfilment fees, with strategies to minimise expenses without compromising service quality. By understanding these costs, businesses can make informed decisions to optimise their logistics operations while improving their bottom line.
Understanding 3PL and Its Importance
What is a 3PL?
Third-party logistics (3PL) refers to the outsourcing of eCommerce logistics processes to a third-party business, such as inventory management, warehousing, fulfilment, and shipping. A 3PL provider is essentially a specialist company that offers comprehensive management of various logistics services including distribution, storage, and transport, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies rather than the complexities of supply chain management.
Key Services Provided by 3PLs
3PL providers deliver a diverse array of services to ensure efficient supply chain management. The primary services include:
- Procurement and Inventory Management: This involves ordering and receiving goods from suppliers, managing inventory levels, and ensuring that goods are available when needed. 3PLs handle the logistics of transporting goods from the supplier to their warehouses and manage the storage of these goods until they are required for distribution.
- Order Fulfilment and Distribution: 3PLs take charge of the entire order fulfilment process, which includes receiving orders, picking and packing goods, and arranging for their shipment to the end customer. This process not only streamlines operations but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery of products.
- Warehousing: 3PL providers offer various warehousing solutions such as public and contract warehousing, specialised storage for sensitive products, and high-security options for valuable goods. These services are backed by advanced in-warehouse tracking systems to facilitate easy storage and retrieval.
- Transportation: They manage the transportation of goods using various methods such as cross-docking, intermodal transport, and comprehensive freight management. This includes optimising fleet operations and utilising advanced tracking systems to monitor the movement of goods.
- Supplementary Services: Beyond traditional logistics services, 3PLs also provide supplementary offerings like reverse logistics, IT systems integration, inventory auditing, and more, which add significant value to their primary logistics functions.
By leveraging these extensive services, 3PL providers play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain operations, allowing businesses to save on costs and improve their operational throughput.
Factors Influencing 3PL Costs
Several elements play a crucial role in determining the costs associated with third-party logistics (3PL). From the geographic location of warehousing facilities to the specific service level agreements (SLAs) required by businesses, understanding these factors can help in effectively managing and potentially reducing 3PL expenses.
Warehouse Size and Capacity
The size and capacity of the warehouse directly influence costs. Larger facilities require more infrastructure, such as storage racks and equipment, leading to higher expenses. It is vital for businesses to select a warehouse that aligns with their needs to avoid overspending on unused space or facing constraints due to undersized facilities.
Handling and Storage Requirements
Products requiring special handling conditions, like temperature control or secure storage for hazardous materials, lead to higher costs. These specialised facilities necessitate advanced infrastructure and adherence to strict regulatory standards, increasing overall expenses.
Inventory Volume and Management
The volume of inventory stored and the complexity of its management affect 3PL costs. Higher inventory levels generally increase storage fees, while effective inventory management practices can optimise these costs by ensuring efficient turnover rates.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
The complexity of SLAs can significantly affect costs. Demands for faster order processing or additional services like kitting and packaging increase service charges. Aligning SLAs with business objectives while managing cost implications is crucial.
Technology and Automation
3PL providers equipped with advanced warehouse management systems and automation technologies may charge more, but these tools can also enhance operational efficiency and accuracy, potentially offsetting the higher fees through reduced labour costs and improved service quality.
Bundled Services
Bundling warehousing with transportation and distribution services can offer cost advantages, depending on the scale and complexity of distribution needs. Assessing the potential for cost savings through service bundling is essential.
Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
Seasonal peaks in demand can lead to increased warehousing costs, as providers may adjust pricing models to accommodate higher demand. Effective planning and forecasting are necessary to manage these cost variations.
Customisation and Flexibility
The degree of customisation and flexibility in warehousing services also influences costs. More tailored services typically come at a premium, requiring a balance between customisation and cost efficiency.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive dynamics within an industry can affect 3PL pricing. In competitive markets, providers might offer more favourable rates to secure business, whereas pricing could be less negotiable in less competitive settings.
Types of Fees
3PL systems involve various fees, including setup, handling, storage, and transportation fees. Understanding these fees is crucial for budgeting and cost management.
Variable vs Fixed Pricing Models
3PL providers may offer variable or fixed pricing models. Variable pricing adjusts based on usage and can be cost-efficient during periods of lower demand. Fixed pricing offers predictability and stable margins but may lead to overpayment during low order volumes. Weighing the pros and cons of each pricing model helps businesses choose the most suitable option for their needs.
Breakdown of Common 3PL Fees
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees encompass a range of tasks including product unloading, inventory counting, quality inspections, data entry, and physical storage. These fees can vary widely depending on the method of charging: per unit, per pallet, per order, or even per container. For instance, typical charges might range from £1.29 to £2.50 per carton, £5.25 to £10 per pallet and £190 to £600 per container depending on size and contents.
Storage Fees
Storage fees are calculated based on the amount of space used in the fulfilment centre’s warehouse. These fees can be charged per pallet, per bin, or based on cubic meterage. Some fulfilment centres, like Total Fulfilment, cubic meterage will be analysed daily. Meaning, if you sell x amount on day 1, that freed up space won’t be chargeable the following day. Monthly charges per pallet can range from £6.30 to £31.50, depending on factors such as location and special warehouse requirements like climate control. For centres that offer “Cubic Meterage Per Day”, you can expect to pay anywhere from £0.28 to £0.60.
Pick & Pack Fees
The pick and pack fees cover the costs of selecting items from inventory and preparing them for shipment. This fee structure might include a per order fee plus an additional charge per item picked. For example, a typical fee could be £1.55 per order plus £0.50 per additional item. Therefore, a two-item order would total approximately £2.05. Some fulfilment centres might charge separately for packing materials, adding to the overall cost of order fulfilment.
Packaging Costs
The fees are for the material cost of the packaging medium, which vary from mailers to boxes, in different sizes. For a small mailer (40x50cm) you can expect to pay anything from £0.08 to £0.20 a package, and for a large box (50x40x40cm), £1.57 to £2.95.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are a significant part of 3PL costs, encompassing both inbound and outbound logistics. Inbound shipping might include charges for freight services such as customs clearance and delivery to the warehouse, while outbound shipping involves sending orders from the warehouse to customers. Shipping costs vary widely and can be influenced by factors such as carrier rates, shipping volume, and the physical characteristics of the shipped items. Discounts may be available through the fulfilment centres accounts with carriers. Here’s an example of a fulfilment centres various courier shipping costs:
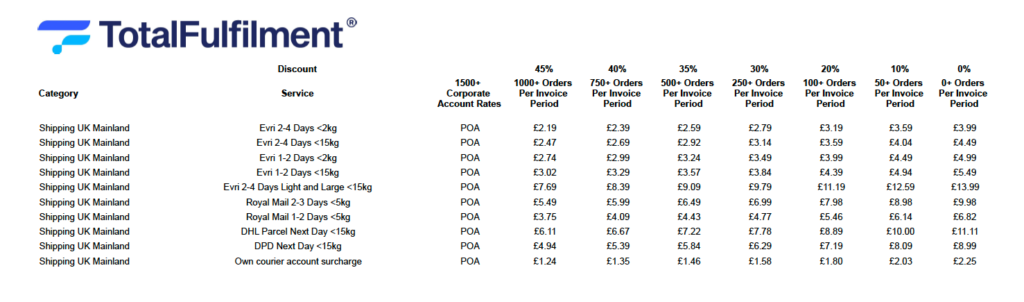
Additional Costs
Initial setup fees for integrating a business’s systems with the 3PL’s systems can range from £75 to £1000, depending on the complexity of the requirements. Account management fees cover ongoing support and might range from free to over £1000 per month. These fees ensure that the 3PL provides adequate support for inventory, orders, and shipments, and may also include customer service for end customers. Additionally, things to consider are software (WMS) costs, that can vary from £35 to £70 per month. On top of that, is marketing materials. Flyers and brochures that can be put into parcels. Costs can be £0.20 to £0.40 per order.
How to Minimise 3PL Costs
Outsourcing non-core functions to third-party logistics (3PL) providers can significantly reduce operational costs by leveraging their expertise in warehousing, order fulfilment, and shipping. By delegating these tasks, businesses can save on personnel, equipment, and other operating expenses, which enhances overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Negotiation Tips
Effective negotiation with carriers is crucial for reducing transportation costs. Businesses should explore various transport options and negotiate diligently to secure the most cost-effective shipping rates. Building good relationships with carriers and regularly reviewing and optimising transport arrangements can lead to substantial savings and contribute to overall cost reduction in logistics operations.
Choosing the Right 3PL Provider
Selecting a 3PL that aligns with the scale of your business is crucial for ensuring the quality and cost-effectiveness of the partnership. It is important to evaluate specific requirements such as order volume, product complexity, and geographic coverage. Additionally, the strategic placement of 3PL warehouses can influence supply chain efficiency, customer satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness. Proximity to suppliers and target markets can enable faster fulfilment and reduce transportation costs.
Cost-Saving Strategies
Utilising shared warehousing models allows businesses to pay only for the space and services they use, scaling costs in proportion to their needs. Partnering with a 3PL that already has a Warehouse Management System (WMS) can also avoid the high costs of purchasing and implementing such technology. Additionally, the Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) model can be beneficial, where 3PLs store goods and perform just-in-time delivery, which maximises production space and throughput at the factory.
Implementing cross-docking services through 3PLs can minimise the costs and time associated with long-term warehousing, allowing for more efficient distribution processes. Moreover, businesses can achieve further cost reductions by using third-party services for functions such as freight bill auditing and utility bill auditing, which can lead to savings, refunds, and better rates.
By adopting these strategies and carefully selecting and negotiating with 3PL providers, businesses can significantly minimise their logistics costs and enhance the overall efficiency of their supply chain operations.
Conclusion
Optimising 3PL expenses without sacrificing quality involves understanding the various factors driving these costs. From warehouse locations to service level agreements, businesses must make informed decisions to align with their logistical and financial needs.
By learning how to negotiate with carriers, choose the right 3PL provider, and apply cost-saving strategies like shared warehousing and cross-docking, companies can improve operational efficiency and financial health. Additionally, effective collaboration with 3PL providers helps ensure smooth logistics to meet customer expectations and stay ahead in the competitive market.






